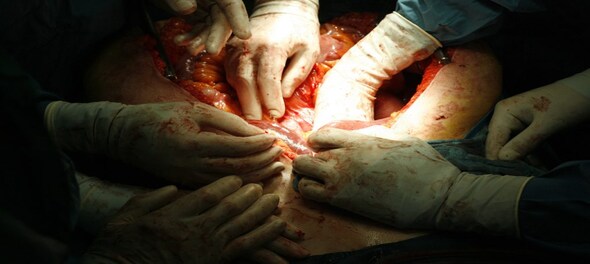
Organ transplantation is a medical marvel that has revolutionised the field of healthcare, offering a lifeline to countless individuals suffering from end-stage organ failure. Through the selfless act of organ donation, the lives of both donors and recipients are transformed, giving hope and a chance at a healthier future. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of organ donation and transplantation, shedding light on the process, benefits, challenges, and ethical considerations surrounding this life-saving practice.
Organ donation —the gift of life
Organ donation is the process of willingly giving a functional organ or tissue from one person, known as the donor, to another, known as the recipient. Organs that can be donated include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, pancreas, and intestines, among others. Tissues such as corneas, skin, bones, and tendons can also be donated to improve the quality of life for individuals in need.
Donation can occur from both living and deceased donors. Living donors can give certain organs, such as a kidney or a portion of their liver, while deceased donors provide organs after their death, usually in cases of brain death or circulatory death. The decision to become an organ donor can be made during one's lifetime or by their family after their passing.
The transplantation process
Organ transplantation is a meticulous and intricate procedure that involves a collaborative effort among medical professionals. The process begins with identifying a suitable organ match for the recipient. Factors such as blood type, tissue compatibility, size, and medical urgency are carefully considered to ensure a successful transplant.
Once a matching organ is found, the recipient undergoes a thorough medical evaluation to assess their overall health and determine their readiness for surgery. Surgical teams then work meticulously to extract the donated organ from the donor's body, preserving its viability. Simultaneously, the recipient's medical team prepares them for the transplant procedure.
The actual transplantation surgery is a culmination of years of medical research, innovation, and expertise. Surgeons skillfully connect blood vessels, sew together tissues, and ensure proper functioning of the transplanted organ. After the surgery, recipients receive immunosuppressant medications to prevent their immune systems from rejecting the new organ.
Benefits and challenges
Organ transplantation offers numerous benefits, extending and enhancing the lives of those facing organ failure. Patients who receive transplants often experience improved quality of life, increased longevity, and the ability to engage in activities they were previously unable to enjoy. These life-altering benefits extend to families and loved ones as well.
However, the field of organ transplantation is not without challenges. One of the most significant hurdles is the shortage of available organs. The demand for organs far outweighs the supply, leading to lengthy waiting lists and, tragically, the loss of lives. Efforts to raise awareness about organ donation and streamline the donation process are ongoing, aiming to bridge this gap.
Ethical considerations and public perception
Organ transplantation raises various ethical questions, ranging from consent and equity to the definition of death. Determining brain death or circulatory death and obtaining valid consent from donors or their families are critical ethical components of the process. Public perception and cultural beliefs surrounding organ donation also influence donation rates and practices.
Cultivating a culture of informed consent and open communication is essential to address these ethical concerns and increase organ donation rates. Education campaigns, community outreach, and collaboration between healthcare professionals, religious leaders, and policymakers can play a pivotal role in shaping public attitudes and fostering a more supportive environment for organ donation.
The miracle of second chances
Organ donation and transplantation represent a powerful testament to human compassion, scientific advancement, and the remarkable capacity of medicine to save lives. As medical knowledge and technology continue to evolve, the future holds promise for even more successful transplants, improved patient outcomes, and expanded access to life-saving treatments.
To truly harness the potential of organ transplantation, it is essential for society to come together, advocating for increased awareness, education, and policy reforms. By understanding the intricacies of organ donation and transplantation, we can take a step closer to creating a world where the gift of life is accessible to all those in need.
— The author Dr Abhay Sadre, is a Consultant Nephrologist & Transplant Physician at Ruby Hospitals, Pune. The views expressed are personal.
(Edited by : C H Unnikrishnan)
First Published: Sept 26, 2023 8:23 AM IST
Check out our in-depth Market Coverage, Business News & get real-time Stock Market Updates on CNBC-TV18. Also, Watch our channels CNBC-TV18, CNBC Awaaz and CNBC Bajar Live on-the-go!


PM Modi visits Ram Mandir for first time since 'Pran Pratishtha', offers prayers before roadshow
May 5, 2024 8:59 PM
Visiting temples, obliging selfie requests, jabbing rivals – Kangana Ranaut is wooing voters on campaign trail
May 5, 2024 8:23 PM

