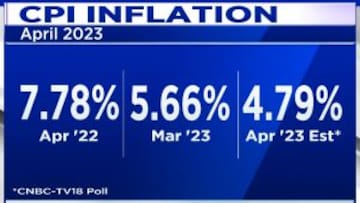
India's annual retail inflation cooled to an 18-month low in April, below the Reserve Bank of India's upper tolerance level of 6 percent, as food prices softened. Inflation as measured by the annual change in the consumer price index (CPI), eased to 4.70 percent in April from 5.66 percent in the previous month, government data showed on Friday.
The central bank targets a range of 2 percent-6 percent. The country’s headline inflation remained within the tolerance range of the RBI for the second consecutive month.
The
CPI inflation was forecast to have fallen to 4.79 percent in April from 5.66 percent in March, according to
CNBC-TV18's poll of economists.
The consumer food
price index (CFPI), which accounts for nearly half of the overall consumer price basket, moderated to 3.84 percent, down from 4.79 percent in March 2023.
"April 2023 was marked by above-average rainfall and lower than normal temperatures, which helped to keep prices of some vegetables under check. Notwithstanding the mixed month-on-month trends across food items, the YoY CPI food inflation is likely to remain subdued in May 2023 aided by the sustained high base (+8.0 percent in May 2022). With El Nino expected to materialise only in the second half of the monsoon season as per the IMD, kharif sowing may not be impacted. However, any subsequent deficiency in monsoon rainfall could affect kharif yields and winter sowing, and thereby food inflation, which poses a risk to the CPI inflation trajectory," said Aditi Nayar, Chief Economist and Head of Research & Outreach, ICRA.
"Although the impact of a favourable base effect related to escalation of geopolitical conflict is likely to have peaked in April 2023, ICRA foresees the CPI inflation to remain range-bound at 4.7-5.0 percent in May-June 2023. With a dip in the CPI inflation below 5.0% and surprisingly subdued IIP growth, we foresee a high likelihood of a pause from the MPC in its next meeting. However, a pivot to rate cuts appears quite distant," the ICRA Chief Economist said.
Further, she added: "The timeliness and intensity of the monsoon onset would be known when the MPC meets at its next scheduled meeting in June 2023, which would feed into whether its CPI inflation projection of 5.2% for FY2024 needs to be modified."
The rural inflation in April stood at 4.68 percent, and the urban inflation came in at 4.85 percent.
”Food inflation was a mixed bag on the month, with cereals and vegetables easing, whilst pulses and milk rose. Lower energy prices continue to filter through to fuel components,” wrote Radhika Rao, senior economist at DBS Bank. ”With inflation off the boil besides core (inflation), the RBI is likely to remain on an extended pause,” Rao said.
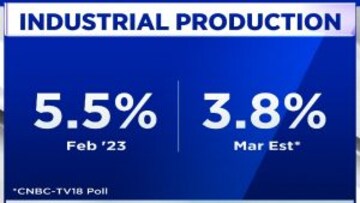
IIP growth declines to 1.1% in March
On the other hand, India's industrial output, as measured by the index of Industrial production or IIP, in March declined to 1.1 percent, data from the Ministry of Statistics showed today. As per CNBC-TV18's poll, the March IIP data was expected to decline to 3.8 percent. In the previous month, February, the IIP was 5.5 percent, and the average from April to February was also 5.5 percent.
"Most of the available high frequency indicators recorded a deterioration in their year-on-year performance in April 2023, relative to March 2023, partly on account of the unseasonal rainfall seen during the month. Accordingly, ICRA expects the on-year IIP growth to remain sub-2 percent in that month," said Nayar.
Factory output measured in terms of IIP rose 2.2 percent in March 2022.
The data released today by the National Statistical Office (NSO) showed that the manufacturing sector's output grew 0.5 percent in March 2023.
Mining output increased 6.8 percent during the month under review, while power output declined by 1.6 percent in March.
The RBI which kept its main interest rate unchanged at 6.50 percent at the April meeting was forecast to extend the pause until at least the end of this year, marking an end to the central bank's modest tightening cycle. The central bank has so far hiked the benchmark repurchase rate by 250 basis points cumulatively since May 2022. In the last fiscal, which ended March 31, 2023, the RBI had projected an average annual retail inflation at 6.5 percent.
First Published: May 12, 2023 5:36 PM IST