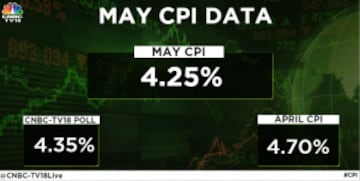
India's annual retail inflation continued to trend lower in May this year, staying well below the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) upper tolerance limit for the third consecutive month, driven largely by base effects. The central bank targets an inflation range of 2 percent-6 percent. The CPI inflation was forecast to have fallen to 4.35 percent in May from 4.7 percent in April, according to CNBC-TV18's poll of economists.
Inflation, as measured by the annual change in the consumer price index (CPI), eased to 25-month low of 4.25 percent from 4.7 percent in the previous month, data released by the National Statistics Office (NSO) showing on Monday evening.
Sequentially, the inflation remained unchanged at 0.51 percent in May.
Food inflation, which accounts for nearly half of the overall consumer price basket, moderated further to 2.91 percent compared with 3.84 percent in the previous month.
"The CPI inflation print for May 2023 eased to a softer than expected 20-month low of 4.3%, as against our expectation of 4.6% for the month, with the positive surprise chiefly driven by the food and beverages segment. Nevertheless, concerns loom on the horizon regarding the potential impact of a sub-par monsoon on food inflation in the second half of this fiscal," said ICRA Chief Economist Aditi Nayar.
"The May 2023 retail inflation rate of 4.25 percent was in line with our forecast. The sharp decline in inflation in recent months is primarily attributable to the favourable base effect rather than a month-over-month loss of inflationary momentum. In addition, the core inflation rate for goods continues to be relatively elevated," said Sujan Hajra, Chief Economist at Anand Rathi.
"Our estimates indicate that, despite remaining close to 4 percent, retail inflation is unlikely to consistently fall below 4 percent over the next 12 months. In light of the lack of a significant loss of inflationary momentum from month to month, the elevated core goods inflation, and the retail inflation remaining above the RBI's inflation target, we anticipate that the RBI will remain in an extended pause mode and that there will be no rate cuts during the remainder of the current year and probably the first half of the following year as well," Hajra said.
Apart from base effects, the drop in numbers can be attributed to moderation in food and fuel prices. The easing prices of cereals and vegetables in addition to lower energy prices have also pulled back the inflationary levels last month.
Also, a sharp fall in global prices of LPG and Kerosene can be linked with the lower fuel inflation in May.
India’s rural inflation stood at 4.17 percent in the last month while urban inflation stood at 4.27 percent.
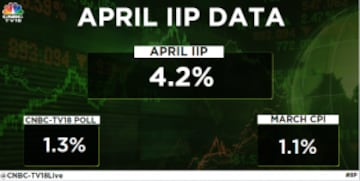
April IIP rises sharply
On the other hand, India's industrial output, as measured by the index of Industrial production or IIP, in April rose to 4.2 percent from 1.1 percent in March, data from the Ministry of Statistics showed today. As per CNBC-TV18's poll, the April IIP data was expected to decline to 1.3 percent.
IIP growth was 6.7 percent in April 2022.
The manufacturing sector's output grew 4.9 percent in April 2023 as against 5.6 percent a year ago.
Power generation fell by 1.1 percent in April this year as compared to a growth of 11.8 percent.
Mining output surged by 5.1 percent during the month under review as against a growth of 8.4 percent in the same period a year ago.
"The IIP for April 2023 also surprised on the upside, printing at 4.2 percent in the month in spite of the unseasonal rainfall. The year-on-year performance of most available high frequency indicators improved in May 2023 relative to April 2023, which should support a 4-6 percent expansion in May 2023," the ICRA economist said.
Last week, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) left the main policy instrument, repo rate, unchanged at 6.50 percent for the second consecutive monetary policy, giving relief to home, vehicle and other retail borrowers from an increase in equated monthly instalments (EMIs).
RBI's call to keep the repo rate unchanged was taken unanimously by the six Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) members as inflation continues to remain above the 4 percent target. The RBI has been mandated by the Central government to keep CPI inflation at 4 percent with a band of +/- 2 percent.
First Published: Jun 12, 2023 5:34 PM IST