
Delhi took an exciting step toward cleaning its air with the notification of the much-awaited Delhi EV Policy on August 7, 2020. The notification of the policy marks the official commencement effective immediately. The policy aims to address the problem of deteriorating air quality in Delhi, which threatens the quality of life and health of the national capital’s residents.
Vehicular pollution is one the major sources of pollutants in Delhi. The emissions source apportionment study conducted for Delhi highlights tailpipe emissions contributing to about 40 percent of PM2.5, 20 percent of PM10, and more than 80 percent of NOx and CO in ambient air pollution.
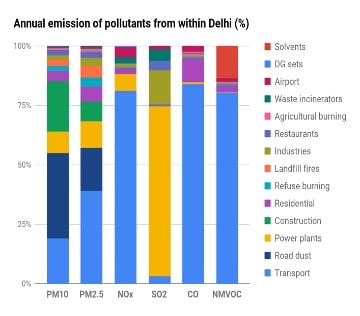 Source: Source Apportionment of PM2.5&PM10 of Delhi NCR for Identification of Major Sources, ARAI and TERI, Aug 2018
Source: Source Apportionment of PM2.5&PM10 of Delhi NCR for Identification of Major Sources, ARAI and TERI, Aug 2018During the announcement of the policy, Delhi’s Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal highlighted the need to adopt measures that can put the city's mobility system on an energy-efficient and low-emissions trajectory. If the policy achieves its target of 25 percent registration of electric vehicles (EVs) in new vehicle sales by 2024, approximately 500,000 EVs of various kinds will be operating in the city. This would translate into a reduction of 159 tons of PM 2.5 in Delhi and a reduction of 4.8 million tons of CO2 emissions, equivalent to avoiding CO2 emissions from nearly one lakh petrol cars over their lifetime.
Pillars of the Delhi EV Policy
Driving EV Adoption through fiscal and non-fiscal incentives: In order to address the high-upfront cost of EVs (compared with internal combustion engine
In addition to the financial incentives, the Delhi EV policy also provides non-fiscal incentives in the form of road tax and registration fee waivers and green-registration plates. Non-fiscal incentives are provided to accelerate demand creation without burdening the government exchequer. The policy also uses regulatory instruments like open permits for e-autos, traffic and parking related exemptions for e-carriers, and regulatory go-ahead on plying of e-bike taxis and shared two-wheelers to create demand for EVs in these different segments.
Addressing barrier to fast-track charging infrastructure deployment: The policy commits to creating an enabling environment for the provision of private and public charging/swapping infrastructure. The policy has provisions for financial incentives to support slow charging (or home charging). Additionally, the EV charging tariff is kept at Rs 4.60 ($0.061), which is one of the lowest in India, to encourage the adoption of standardised charging equipment since the commercial electricity tariff would be as much as twice as expensive as the EV tariff.
Creating a Recycling Ecosystem for batteries: The policy aims to encourage the re-use and recycling of EV batteries that have reached the end of their life. Adoption of the targeted number of EVs may result in an enormous amount of batteries that need to be recycled or to be utilised for secondary usage such as energy storage for large solar rooftop projects. In partnership with energy service providers, the Delhi government aims to develop a framework for the efficient recycling of batteries and the promotion of the second-life of batteries as “power banks” to store renewable energy.
Setting up of State EV Fund: The Delhi EV policy seeks to fund a high proportion of the incentives using the “feebate” concept (i.e., by adopting measures by which inefficient or polluting vehicles incur a surcharge). The policy directs funding through sources like pollution cess, road tax, congestion tax, and other sources such as the environment compensation charge (ECC) to an umbrella, non-lapsable State EV Fund. The policy specifies diverting 50 percent of the total pollution cess (Rs 0.25paise/liter of diesel) collected in Delhi to the State EV Fund instead of the entire amount going to the Air Ambience Fund. The policy also puts a road tax and congestion tax on ICE vehicles.
Creating Jobs in the EV supply chain: The EV Policy envisions job creation as a key outcome. It aims to promote skill development in the electric vehicle supply chain to establish an efficient after-sale ecosystem for EVs in Delhi. Considering that the policy aims to promote about 5 Lakh EVs in Delhi, it has immense potential to create a large number of jobs such as EV drivers, auto-mechanics, charging station operating staff, etc.
Policy Implementation: It will be led by the Department of Transport and the State EV Board, under the leadership of Hon'ble Minister of Transport. The leadership will be responsible for reviewing the performance of various measures under the policy and taking additional measures as necessary for effective implementation. The Policy also commits to working towards creating consumer awareness by creating an outreach plan describing the benefits of EVs.
Delhi’s EV policy by far presents itself as the most comprehensive subnational policy that adopts a systemwide approach to promote the adoption of EVs. It puts equal emphasis on instilling confidence in consumers and industry while ensuring that a public scheme like this invests in modes and assets that will have equitable benefits for all. This positions it on a path of success if the right institutional and procedural mechanisms are put in place rapidly and efficiently. The policy has set an example for developing comprehensive policy frameworks that deal with new subjects and new technologies. The hope is for the policy to deliver and exceed its stated objectives and make the capital EV-ready.
—Akshima Ghate is Director, RMI India and Dimpy Suneja is Consultant, RMI India. The views expressed are personal
First Published: Aug 27, 2020 6:21 PM IST
Check out our in-depth Market Coverage, Business News & get real-time Stock Market Updates on CNBC-TV18. Also, Watch our channels CNBC-TV18, CNBC Awaaz and CNBC Bajar Live on-the-go!


Prajwal Revanna's father in custody for alleged kidnapping and sexual abuse
May 4, 2024 7:53 PM
Delhi, Indore, Surat and Banswara — why these are the most challenging domains for Congress internally
May 4, 2024 1:53 PM
Congress nominee from Puri Lok Sabha seat withdraws, citing no funds from party
May 4, 2024 12:00 PM
Lok Sabha Polls '24 | Rahul Gandhi in Rae Bareli, why not Amethi
May 4, 2024 9:43 AM

